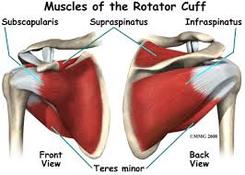
The rotator cuff is subject to stretch injuries, torsional injuries and impact injuries. The majority of rotator cuff tears are due to long-term wear-and-tear and frequently the abnormalities noted on MRI's of the shoulder are pre-existing problems. Acute tears of the rotator cuff are always associated with a history of immediate onset of pain, decreased range of motion and severe sleep dysfunction. These symptoms occur within the first 24-48 hours of an injury, if there is an acute rotator cuff tear as a result of the accident.
The driver of a vehicle who is rear-ended and who is grabbing the steering wheel at the 10:00 and 2:00 positions and placing the elbows in full extension, is subject to rotator cuff trauma. The more difficult cases are those where the vehicle is rear-ended and pushed forward into the vehicle in front, or is pushed off in a direction to the right or left and the driver attempts to regain control. This produces torsional events on the rotator cuff, which can also cause tears. In some cases, the driver is pushed forward and strikes the steering wheel with the anterior part of the shoulder. This can also produce injuries to the bicipital tendon and the anterior aspect of the rotator cuff.
Automobile accident where there is a side impact and the vehicle spins in the opposite direction, when at the same time the driver is attempting to regain control of this changing direction, also puts the rotator cuff at risk because of the rapidly changing direction of the steering wheel.
It is important to notice and memorialize the bruise patterns. Photos of the bruising help identify whether the primary impact collision was from the front, the back, or the side. All persons who are injured in an accident and who complain of shoulder pain with decreased range of motion during the first 24 hours should undergo diagnostic studies. Initially, x-rays should be obtained and based on the x-rays and physical examination, on many occasions an MRI of the shoulder is indicated if the doctor suspects rotator cuff tear. An orthopedic surgeon performing the examination is in a better position because he or she has determined the points of tenderness as well as presence of any impingement abnormalities.
Non-displaced or minimally displaced fractures are treated in a comfort sling and usually do not warrant a surgery. Severe fractures of the clavicle occasionally warrant open reduction internal fixation. The diagnosis of rotator cuff injury can be deceiving within the first 30-45 days, especially in individuals who develop a partially frozen shoulder. The usual treatment focuses on regaining range of motion with physical therapy and a home exercise program.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
