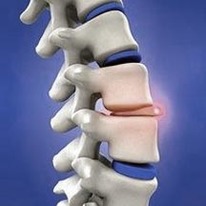
In many cases, a bulging disk may be diagnosed as a condition secondary to another problem. Because a bulging disk does not always cause pain, it may only be found during a routine or diagnostic imaging test such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The medical treatment for a bulging disk is relatively conservative in most cases. Rest and lifting restrictions are common, and a doctor may recommend a combination of heat and ice therapy and anti-inflammatory medications or cortisone injections to alleviate the symptoms.
Back surgery, though not as common, can relieve severe pain caused by compression on the nerves from a bulging disk that becomes herniated.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
